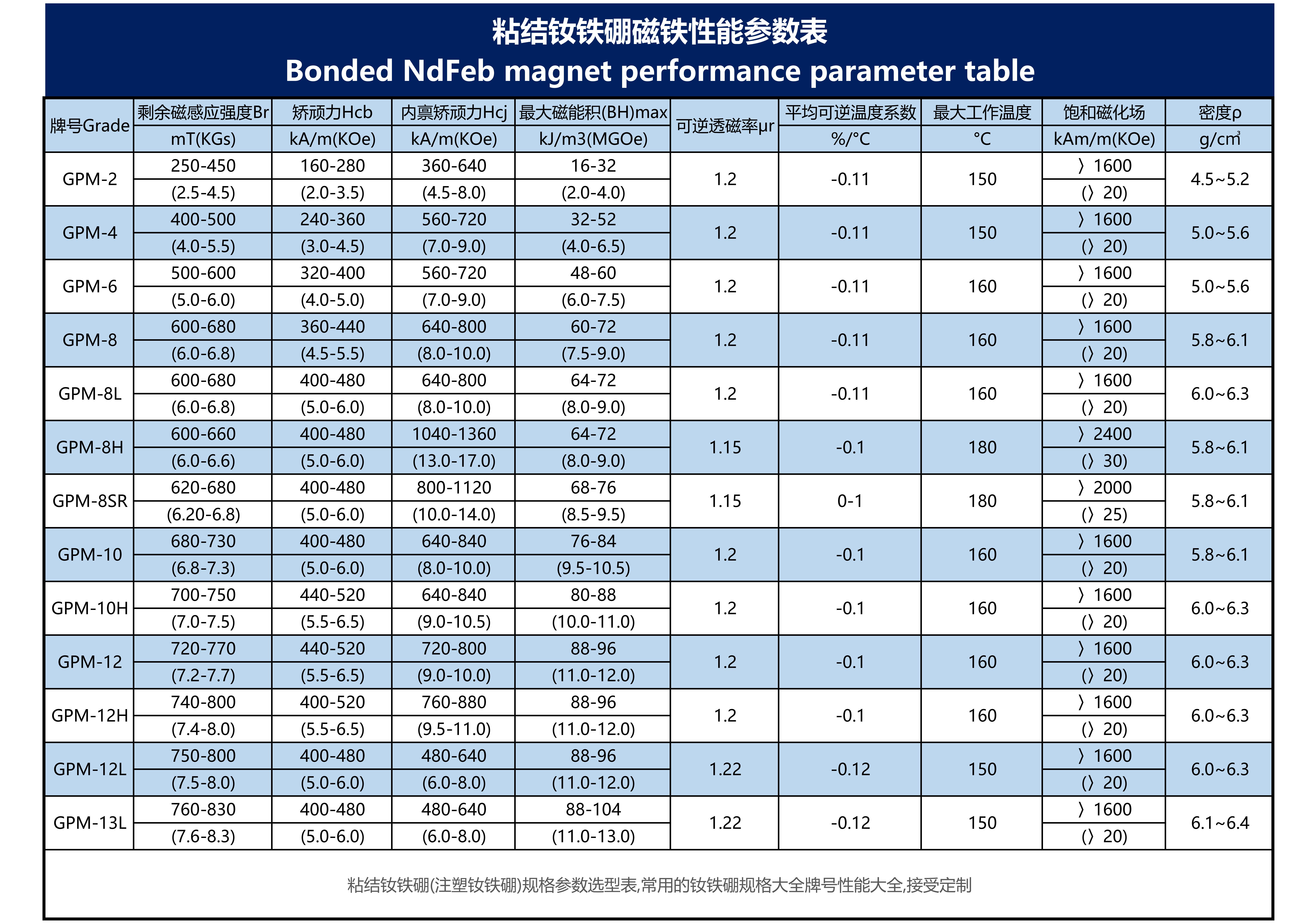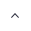
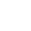


Bonded NdFeB Magnet (Bonded Neodymium-Iron-Boron)
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | NdFeB magnetic powder mixed with resin/plastic, molded via injection or compression. |
| Cost Performance | - Lower magnetic performance than sintered NdFeB. - Low processing cost, suitable for complex shapes and miniaturization. |
| Applications | - Micro-motors (drones, camera shutters). - Consumer electronics (headphone magnets). - Office equipment (printer rollers). - Smart home components. |
| Magnetic Properties | - Low magnetic energy product (6–15 MGOe). - Moderate remanence (Br) and coercivity (Hc). - Poor temperature stability (max operating temp: ≤150°C). |
| Work Environment | - Poor corrosion resistance (requires epoxy resin coating). - Can be shaped into thin-walled or complex parts. - Better vibration resistance than sintered NdFeB. |
Magnetic Performance vs. Cost:
Bonded NdFeB has lower energy product (6–15 MGOe) than sintered NdFeB (30–52 MGOe) but higher than Ferrites (3–6 MGOe).
Cost-effective for mass-producing intricate shapes (no high-temperature sintering required).
Applications:
Bonded NdFeB: Miniaturized, lightweight applications (e.g., consumer electronics, micro-motors).
Sintered NdFeB: High-performance fields (e.g., EVs, wind turbines).
Ferrites: Low-cost, high-volume uses (e.g., household appliances).
Environmental Adaptability:
Temperature resistance (≤150°C) and corrosion resistance (requires coating) are weaker than SmCo (300°C) and AlNiCo (550°C).
Superior vibration resistance and shape flexibility compared to sintered NdFeB.
Key Advantages:
Design Flexibility: Enables thin-walled, complex geometries via injection molding.